One particular compound that has sparked much discussion began with the question, “What is Theobromine?” The scientific, laboratory-centered emphasis on health has led to many important discoveries on the molecular level.
Many people who take an interest in their health are simultaneously learning the detailed microbiology of common foods they are eating, and sometimes the definitions can become complex.
This one in particular was first discovered in 1841 by a Russian chemist named Aleksandr Voskresensky who was studying cacao seeds. He discovered this to be the active compound that gives cacao its stimulating quality.
The chemical’s name is derived directly from Theobroma, which is the genus name of the cacao
. “Theo” is a Greek word that means “god” and “broma”, “food”, which translates to “food of the gods”.
Cacao trees are native to tropical areas in Africa and South and Central America, and the seed crops have been eaten raw for centuries as a natural stimulant, relaxant, aphrodisiac, and for mood regulation.
The value of cacao was so high during a time in the ancient Aztec civilization that the seeds achieved the status of a currency.
While the general use has been known for as long as people have been cultivating the Theobroma cacao trees, scientific specificity now gives us the language and understanding for exactly how these foods directly affect our bodies.
Its technical definition is an alkaloid, which are molecules which contain nitrogen atoms which stimulate the central nervous system.
It is a bitter alkaloid compound, formerly known as xanthosis. In the body, it acts as a mild stimulant, and it has the same effect as a cup of coffee.
Cacao tree seeds are the primary source of this chemical, which may be found in several foods. These beans are the seeds of the cocoa tree, a plant that grows in South America’s tropical areas.
Besides cocoa, many other plants contain it, such as guarana, kola nut, and yerba maté.
How Much of it is present in the bar of chocolate?
Chocolate’s content varies according to the kind of chocolate used. For example, Hershey’s Milk Chocolate and 100% cocoa powder are very different products.
The concentrations in various chocolate and cocoa products are listed below, according to the USDA’s nutritional database:
2634 mg in cocoa powder, unsweetened.
Unsweetened baking chocolate has 1297 mg.
802 mg in dark chocolate (70 percent cocoa).
Twin bar of Mars Twix: 39.9 milligrams
As can be seen, its concentrations are highest in chocolate that contains 100% cocoa or higher.
Does coffee have theobromine
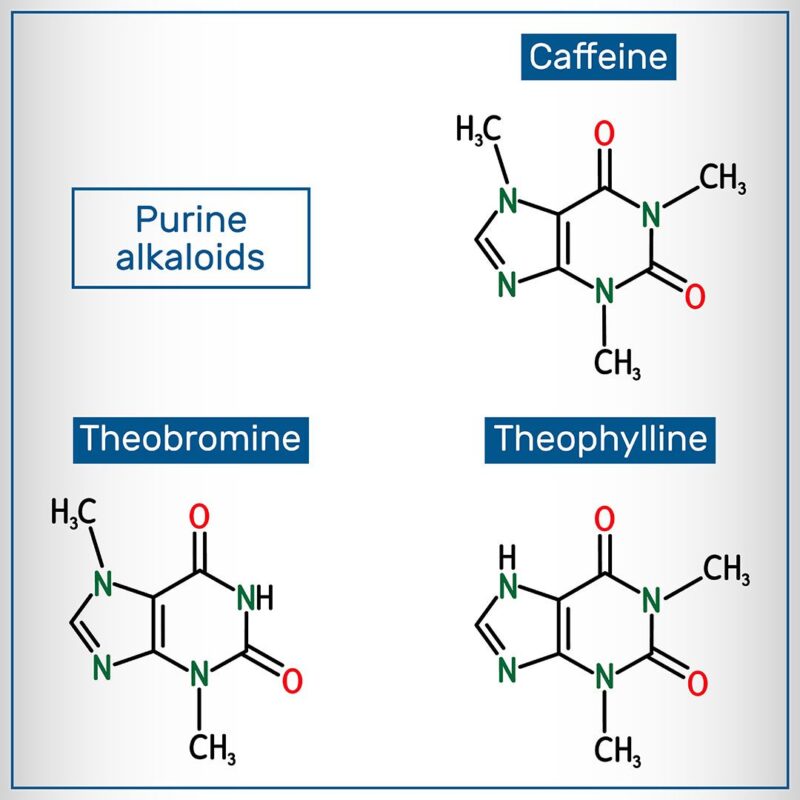
Another alkaloid that is commonly associated with this base nutrient in cacao is caffeine, although there is a minuscule molecular difference.
Both chemicals are called methylxanthines, which are a family of alkaloids. But caffeine has a single methyl group located on a different area of the compound.
The difference is very subtle and the body begins to metabolizes them in a nearly identical way.
Because they are so similar, coffee and chocolate (chocolate is the most common food derived from cacao seeds) are usually grouped together because they originally come from seeds from South American trees.
But this subtle difference between the two actually creates a significant change in terms of health effects to the human body.
Coffee only contains caffeine and is one of the most consumed beverages in the world. It can make one jittery, nervous, overactive, and a single tablespoon of pure caffeine can actually kill you.
But this compound inherent in cacao seeds is around 10 times weaker than caffeine because it binds to the central nervous system in a loose and less intense way, which also makes it longer lasting.
Our bodies absorb the compound slower which releases its effects in a more balanced manner. Because of this slow uptake into the body, people don’t get the same kind of energy crash when consuming chocolate than when consuming even a single cup of coffee.
In addition, as a base chemical it is far less addictive than caffeinated beverages, which give an immediate rush of bodily effects.
Both coffee and chocolate are stimulants, but our main chemical has a more edgy flavor and a less-powerful impact.
Here are some of the interesting facts about it:
The half-life of the chemical is 7.2 hours.
It takes around 7.2 hours for the concentration in the blood to decrease by half.
A person’s unique half-life might range from six to ten hours.
This stimulant may improve attention and focus.
It may increase cholesterol levels.
A decreased risk of cardiovascular disease is generally associated with greater HDL levels. The research found that it had a positive effect on HDL levels.
It provides an increase in mental energy, which acts as a stimulant.
Humans can benefit from it as a psychoactive drug.
As a part of these advantages, it inhibits phosphodiesterases and blocks adenosine channels in the brain. These effects may increase neural activity.
According to research, it has a calming effect on the mind and body. Studying the impact on cognitive performance is also possible.
Anti-inflammatory activities
Oxidative stress-induced inflammation is a significant risk factor for many co-occurring disorders.
Diseases such as Alzheimer’s and type 2 diabetes and cancer and heart disease are thought to be caused by inflammation.
Finally, any exercise that minimizes free radical damage and inflammatory indicators may contribute to a healthy lifestyle and lessen the risk of certain chronic illnesses.
According to a few studies, this chemical seems to offer some benefits in reducing inflammation.
It may help regulate cellular activities by preventing the enzyme phosphodiesterase from functioning. In addition, the medicine seems to lower C-reactive Protein (CRP) levels and the levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the bloodstream.
With its anti-inflammatory properties and ability to control the airways, the chemical has shown promise as a therapy for asthma.
Indirect Benefits
Cocoa powder and dark chocolate are the best sources of this medicament. However, cocoa is the most common dietary source of theobromine for anyone looking to get their hands on it.
Cocoa, which has the most outstanding nutritional content of any item in the human diet, is mostly unknown to the general public.
A single ounce (28 grams) of cocoa, for example, has the following nutritional components:
Manganese: 52%
Copper is 50%.
Magnesium is 33%.
Iron is 24%.
20% of the recommended daily allowance of potassium.
Phosphorus: 20%.
Zinc is 12%.
Vitamin B12: 8% of the recommended daily allowance.
Rarely you do find so many nutrients in such a little quantity of food.
Its primary dietary sources are very nutrient-dense and offer several health advantages on their own.
Theobromine supplement
The best way to ingest this compound is by eating raw cacao seeds or raw unrefined cacao powder, but this is more difficult for those not living near areas where it is grown and processed.
The next best method is to eat chocolate bars that are made with a significant percentage of cacao intact in the bar, from 70% and up.
For those who are not fans of chocolate because of the high sugar content, this powerful compound is also available as straight powdered supplements.
It is commonly labeled on packaging as a fat-burner or may help in weight loss because it stimulates metabolism and an increase in overall energy.
Some other important health effects of this cacao-derived compound are:
Lowers Blood Pressure
One of the first immediate bodily effects is as a myocardial stimulant and vasodilator. This means that it widens the blood vessels so that more blood can flow through.
This effect will take place within an hour of consumption, and taking it over a period of time will have an overall positive effect on heart health.
As a supplement it is a great way to regulate and even lower blood pressure, taking strain off the heart and cardiovascular system as a whole.
Enhances Endurance
Taken as a supplement it also acts as a bronchodilator, which is when the air passages to our lungs are widened allowing for more air to flow into them.
This allows athletes to take in more oxygen while they are performing or working out. The oxygen then travels throughout the rest of the body through the blood cells.
Overall endurance increases and because the muscles are receiving more oxygen they will not become tired or sore as quickly.
The result is that a person will be able to exercise for a longer period of time, be able to build more muscle mass, and when the workout is over the muscles will be able to replenish themselves at a quicker rate.
Improves Sleep Quality
While caffeine will give a quick boost of energy and a crash later, this eventual crash does not guarantee that sleeping will be any easier or as replenishing.
The cacao-derived nutrient, on the other hand, because of its gradual and measured uptake into the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, supports a balanced change in energy levels which has been shown to improve sleep quality and duration.
Aphrodisiac and Mood Enhancer
Chocolate has a reputation for being an aphrodisiac and it is because of this base compound. But besides making someone more “in the mood”, it has the general effect of being a mild antidepressant and improves one’s overall peace of mind.
This is because of the increase in blood flow and energy levels, which takes strain off the body and which can effect our mind in a positive and even a euphoric way.
Health Benefits
Here are some of its common health benefits of it.
Reduces Hypertension
Vasodilation is the enlargement of blood vessels if you’re not already familiar with it.
It aids in the dilation of constricted blood arteries. As a result, it may be used as a treatment for hypertension.
Additionally, it may serve as a diuretic by increasing urine output and decreasing blood volume. Results from several experiments have mainly been positive on this topic.
Supplementing 42 healthy adults with high blood pressure with 979 mg of this product daily was studied in a double-blind, randomized, double-blind research.
For a total of three weeks, the experiment was conducted. Within two hours of ingesting it, blood pressure dropped significantly and consistently. The placebo group didn’t have the same impact as the experimental group.
Strengthens the enamel of the teeth
Using it may have the additional benefit of strengthening the surface of teeth, which is not a direct benefit.
The topical solution has been demonstrated in many tests to increase enamel strength. in some instances, it works as a moderate stimulant
Moreover, it has an energetic effect on the body and raises heart rate dose-dependent. The chemical has been proven to boost attention, focus, and the ability to interpret visual information following consumption.
However, it doesn’t seem to have the "happy" mood-enhancing benefits.
Enhance Sleep
It also does not interfere with one’s ability to sleep, as it makes coffee and has been shown to enhance sleep. It was shown to be the most critical factor in sleep duration.
The drug of love
The human brain contains a tiny yet strong substance called phenylethylamine (PEA). It triggers the release of endorphins.
Serotonin and dopamine are also somewhat stimulated, which increases the experience of sexual arousal and pleasure. It’s also a powerful antidepressant, thanks to melatonin.
In the context of orgasm, it is regarded as the "love drug" since it is present in higher concentrations in the brain during periods of love.
It may be found in other foods as well, and it’s being examined to see whether the concentration in dark chocolate causes these specific emotions and experiences.
Anandamide is a natural chemical found in chocolate and the human body. It is known as "the happiness chemical" because of its ability to activate cannabinoid receptors in the brain, which boost pleasure and motivation.
Theobromine in chocolate
This drug poisons dogs at high enough concentrations. It is poisonous to dogs at 46 to 68 mg/lb. More than half of the canines that take 228 mg/lb of theobromine die.
Your dog’s size, how much this sugary treat he ate, and whether or not he’s been known to be sensitive to it may all play a role in whether he develops an unfavorable response.
It is found in a variety of chocolate products. Here are some of the examples:
There is an average of 44 mg per serving of the milky version (704 mg /lb).
Each ounce of semisweet chocolate chips has 150 milligrams of it (2400 mg for a pound semi sweet treat)
The content in baking chocolate is 390 mg/oz.
Symptoms of poisoning
Symptoms of poisoning may vary from mild to severe. Indicators include:
Vomiting.
Diarrhea.
Rapid heartbeat.
Restlessness.
Hyperactivity.
Even more, urination will be compromised.
Involuntary muscle contractions.
Seizures.
Other signs of neurological disease.
Please call your veterinarian immediately if you feel your pet has ingested it. Your veterinarian is the only one who can recommend the best course of action for your pet.
Side Effects
Contrarily, it is possible to discover no reason to be concerned about a particular chemical in food products. The following are some of the complex’s main worries.
- Headaches and Vomiting
According to the Toxicology Data Network of the National Institutes of Health, a high dose of (800 to 1200 milligrams) might cause adverse effects such as nausea, sweat, and headache.
- Tachycardia
It’s a condition in which your heart beats too quickly when you’re at rest. To raise the heart rate, this medication is a methylxanthine-based stimulant.
The chocolate may harm canines, don’t you realize?
It is primarily because dogs are unable to metabolize it. Large quantities of a compound can be fatal if they are ingested quickly.
Even tiny quantities of chocolate or food containing this drug may be harmful to cats. On the other hand, Cats seem to be more particular about what they eat.
The fatal dosage (LD50) for dogs and cats is roughly 300 mg per kilogram.
Food and supplements containing it should be kept away from animals.The overdose may lead to a variety of undesirable effects. Even in small amounts, it is dangerous to pets, as mentioned above.
Is It Good For Your Body?
Some well-known advantages of its ingestion may be found initially (blood pressure reduction and cognitive improvement).
Inflammation and lipid profiles may potentially benefit from the chemical. To fully understand these concerns, further research is required.
At this intake level, concerns may arise, such as the high sugar content and the risk of replacing more nutritious meals.
While available in powdered supplement form, the most natural way to consume this compound is by eating organic chocolate with high percentages of pure cacao.
Cocoa, which is the most common ingredient used to make chocolate, is a roasted and refined version of pure cacao. In the refining process the cacao will lose much of its beneficial health qualities, so checking the labels for pure cacao is important.
There is much information online about specific scientific breakdowns of the microbiology of ingredients in the food we eat.
Final Thoughts
Researching “What is Theobromine” is important because it can be a solid replacement to caffeine, which on a molecular level is extremely similar but will produce very different effects to our bodies.
It is a chemical with many caffeine characteristics and is an interesting one. Depending on the person and the dosage, it may have beneficial and harmful effects. Foods high in this drug are delicious, and studies show that it has certain health advantages.