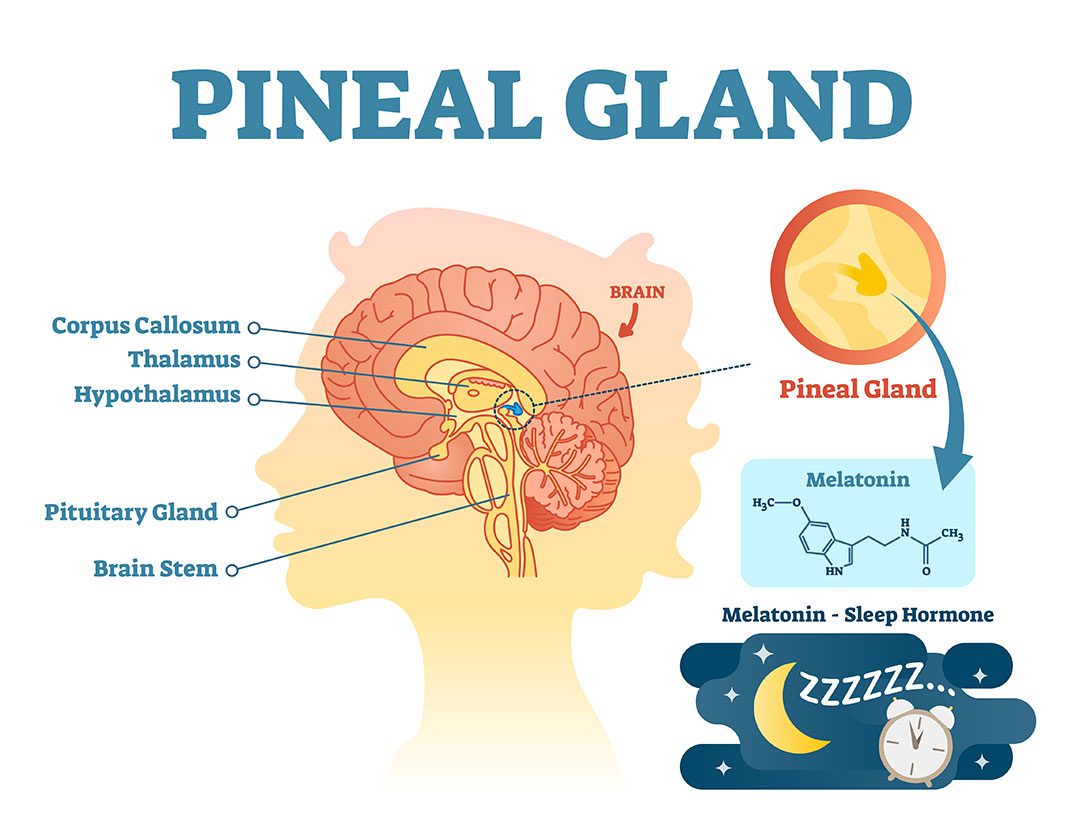
Pineal gland function regulates hormone production and maintains the circadian rhythm, which is our sleep and wake cycle.
This gland also regulates female hormone levels, which may have an effect on fertility and menstruation.
This is partly due to the gland’s production and excretion of melatonin.
The pineal, also called the third eye, is a tiny pine cone-shaped gland located deep within the epithalamus.
It is a component of the endocrine system and aids in the regulation of melatonin, a hormone generated in the brain that aids in nighttime sleep.
This gland was one of the last parts of the human brain to be completely understood.
Function of pineal gland
For a lengthy period, neuroscience was devoted to identifying the distinct functions of the many brain regions.
Nevertheless, it has been discovered by researchers like us that the brain has functional areas that work together rather than one component completing a single task.
There are many facets to this gland.
The secretion of melatonin by the pineal to regulate circadian rhythms and sleep cycles has long been known.
It’s now understood, however, that it serves a much broader purpose.
It regulates hormone impulses to all organs as an endocrine system conductor.
It has effects on all of the body’s systems because of its dual neural-endocrine activity.
What is the function of the pineal gland?
In this article, we’ll discuss the history and recent developments in research that shed light on this gland:
Relation to melatonin
If you suffer from insomnia, it may be a symptom that your pineal is not making enough melatonin.
Some alternative medicine practitioners claim you can detox and stimulate your it to improve sleep and open your third eye.
However, there is no scientific evidence to back these statements.
Using melatonin supplements is one approach to regulate the amount of melatonin in your body. Generally, these will make you feel exhausted.
They may assist you in resetting your circadian rhythm if you’ve traveled to a different time zone or worked a night shift.
Additionally, supplements may assist you in falling asleep more quickly.
For most people, low-dose melatonin supplements are safe for both short- and long-term use.
Normally, dosages vary from 0.2 to 20 milligrams (mg); however, the optimal dose varies by individual.
Consult your physician to determine if melatonin is right for you and the appropriate dosage.
The side effects of using melatonin include:
-
Tiredness and sleepiness
-
Confusion
-
Anxiety
-
A groggy feeling in the morning
-
Intense and vivid dreams
-
A little increase in blood pressure
Cardiovascular health
Melatonin and cardiovascular health have been linked in previous studies.
Melatonin released by this gland has been shown to have a favorable effect on your heart and blood pressure, according to researchers.
However, additional research is required before melatonin is considered a cardiovascular disease treatment.
Female hormones
There is some proof that light exposure and melatonin levels associated with it may have an impact on a woman’s menses.
Melatonin deficiency may also contribute to the development of irregular menstrual periods.
Since studies are restricted and frequently outdated, additional research is required.
Mood regulation
Your pineal’s size may suggest your susceptibility to certain mental disorders.
According to one study, having a smaller one may raise your risk of getting schizophrenia and other mental problems.
Additional research is necessary to better understand how its volume affects mood disorders.
Cancer
According to certain studies, cancer may be linked to a deficiency in gland activity.
Overexposure to light has been linked to cell damage and a higher risk of colon cancer in rats, according to a recent studyTrusted Source.
Another studyTrusted Source, discovered evidence that melatonin may enhance the outlook for cancer patients when administered in conjunction with standard treatments.
Individuals with more advanced cancer cells may be more susceptible to this.
Melatonin’s role in tumor development and prevention necessitates additional study.
Understanding Circadian Rhythms
The pineal, which regulates the body’s circadian cycles, is essential to our internal clocks.
At the same time every day, people go through their daily cycle of feeling tired or drowsy, waking up, and staying attentive due to their circadian rhythms.
The gland produces melatonin, the hormone in charge of regulating circadian rhythms.
People manufacture melatonin based on the amount of light they are exposed to.
During the night, it secretes more melatonin, which is why Melatonin plays a role in sleep.
Natural sleep aids such as melatonin are available from various supplement companies.
Some researchers believe that the link between melatonin and sleep is more complicated than previously thought, based on study done on rats.
Despite having their glands surgically removed, these rats exhibited no distinct behavior.
The researchers concluded that its functioning is more intricate than previously understood and may differ from animal to animal.
Pineal Malfunctions
A malfunctioning one can result in hormonal imbalance, which can have a number of adverse impacts on the body, including altered sleep patterns, irregular menstruation cycles, and fertility issues.
When it produces inadequate hormones, the individual may have insomnia, nervousness, increased estrogen/progesterone ratio, immunological suppression, and decreased body temperature.
On the other hand, when it overproduces melatonin, an individual will experience abnormally low blood pressure, decreased estrogen/progesterone ratios, and insufficient thyroid and adrenal gland activity.
Pineal gland calcification (hardening), viral infections, bacterial infections, toxins, heavy metals, chemicals such as mercury and fluoride, and parasites are all possible causes of gland failure.
Its placement (in the brain) raises the risk of additional organ issues if a person gets a brain tumor. Pineal cell tumors, gliomas, and germ cell tumors are three types of common cancers.
Connection with Light
When answering the question; what is the function? The relationship between the pineal and light is evident.
Each of the eye’s three glands is extremely sensitive to light and responds accordingly.
Prior to 2002, scientists were aware of the cones and rods being involved for color and low light perception.
They discovered a third eye receptor, melanopsin, in 2002.
Melanopsin is a light-sensitive pigment located in the retina cells. Melanopsin delivers information to the hypothalamic SCN (suprachiasmatic nucleus).
The SCN is in charge of circadian rhythm regulation, which affects our alertness, tiredness, temperature, hormone levels, and digestive functions.
The gland gets signals from the hypothalamus to activate and initiate or terminate cortisol and melatonin production in response to the latter’s acquisition of information about the presence or absence of light.
The pituitary, retina, and SCN are all affected by changes in melatonin levels. The pituitary releases vasopressin in response to light, which causes the SCN to adjust our circadian clock.
We are all light receptors, according to the latest research.
The gland and the SCN get signals to cease melatonin production whenever light shines on any region of our body.
Because of the amount of ambient light in our environment, our systems are unable to obtain deep relaxation, which only occurs in complete darkness.
Removing sources of light from bedrooms has been reported to improve health, provide better sleep, activate it, and restore the body’s natural equilibrium by many.
Disorders
Calcification impairs the gland’s ability to function.
A buildup of fluoride in the gland causes the formation of phosphate crystals, which harden the gland.
Melatonin production is disrupted by the hardening of the gland, which results in a disrupted wake-sleep cycle.
Fluoride hardening has been shown to accelerate the sexual development of children, particularly girls.
Chlorine and bromine, as well as calcium supplements, can build up and harm it.
It and other tissues can become calcified if the body does not get enough vitamin D.
Some of the most effective first attempts to reduce health risks involve using fluoride-free toothpaste and avoiding tap water.
-


Tooth Hardening Theobromine Toothpaste
$16.00 — or subscribe and save up to 10%Rated 5.00 out of 5Discover the future of oral…
Additionally, consuming calcium-rich meals rather than taking calcium supplements is preferable.
Natural Remedies
The gland is constantly under attack from pollutants contained in the chemicals and foods we eat and the stress-related molecules created by our bodies in today’s environment.
Hardening of it decreases its ability to operate normally.
In order to preserve this vital organ, there are a few things we may do:
-
Our first priority should be prevention, which may be accomplished by removing hazardous items from your surroundings, which might include food, drinks, the goods you use, and your living space in general.
-
Basking in the sun (ideally at sunrise and sunset) helps activate the work of the gland in addition to stimulating your thoughts. Natural light stimulates it, causing it to create serotonin, which is important for energy levels and emotional stability.
-
You can assist in decalcifying by avoiding junk food, reducing your exposure to fluoride, and eating enough raw, healthful foods.
Conclusion
For years, the function of this gland remained unclear.
It is now widely recognized as the master conductor of the nervous and endocrine systems.
There are few processes in the body that the gland does not influence due to the cross-function of melatonin, sleep, and endocrine hormone secretion.
Therefore, pineal gland function is critical for your general health.