What is the pineal gland and what does the it do? It is a gland located in the brain and its biological importance is very high, as one of its main functions is responsible for the secretion of melatonin.
We took some time to looking into this subject matter, let us know if it was helpful.
This gland and hypothalamus together control sexual desire, thirst and hunger.
Its functions remain active in healthy people, but when excessive stress occurs, as well as anxiety or fear, constipation can occur.
It also produces dimethyltryptamine (DMT), a psychedelic substance that is capable of producing very specific effects on our perception of things by expanding space and time. All this is possible, especially during the REM phase of sleep.
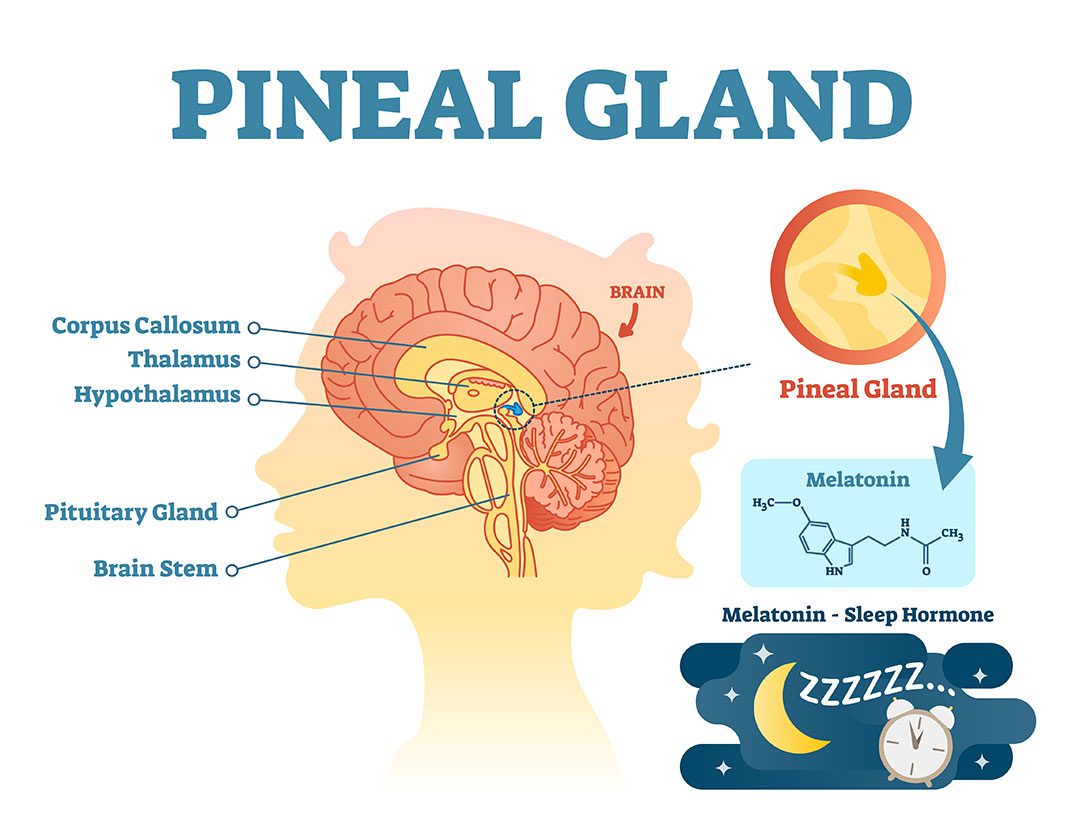
It is an endocrine gland in the brain, located between the cerebral hemispheres, when healthy, it does not exceed the size of a pea.
This gland secretes melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxy-tryptamine), which regulates the circadian cycle, more specifically the sequences of wakefulness and sleep.
Melatonin in animals regulates the function of sex drive, behaviour, fur growth, camouflage and hibernation.
In a healthy human being, this gland and melatonin have several important functions.
In addition to having a strong effect on the circadian cycle, the pineal is also responsible for modulating photoperiodic, annual functions in every healthy human being, so it is most responsible for biorhythm cycles.
This gland is activated by light and cannot produce melatonin if we sleep in a lighted room. Even if that light is as small as, say, dim light on a smoke detector.
The gland works in harmony with the hypothalamus, the gland that determines our desire to eat, drink and it controls the biological clock that determines the ageing process.
Although the hypothalamus occupies only 1% of the brain, it controls vital functions, including heart rate, blood pressure, etc..
It also controls the autoimmune nervous system and controls the endocrine system through the pituitary gland. The hypothalamus also plays an important role in activating emotions and motivation.
What does the pineal gland secrete?
It can secrete melatonin only when we are relaxed, relaxed and asleep. Melatonin can even be secreted during meditation and visualization.
Interestingly, the melatonin molecule has the same structure as the LSD molecule, but while melatonin is a stimulant of rest, pleasure, and relaxed thinking, LSD has psychedelic and often devastating hallucinogenic properties.
So far, there is no official organization that regulates melatonin intake as an aid in regulating the circadian cycle and relaxation, but it is known how much melatonin helps in creating healthy sleep, unlike many negative effects of other artificial sleeping pills and insomnia treatment.
Some research suggests that latency time is significantly reduced when taking melatonin, so it is recommended to take this natural compound 30-60 minutes before going to bed. But also taking melatonin is recommended only for people over 18 years of age.
All people who have problems with light, restless sleep or insomnia are recommended to take melatonin.
Problems with sleep, sleepwalking or insomnia most often occur when we are under stress, and the disorders become stronger and more pronounced the stronger the stress and the longer we are under constant stress.
If we cannot sleep normally or if we do not sleep, there are many mental and physical disorders that can cause various diseases.
Melatonin is also recommended for people who suffer from the effect of "jet lag" of rapidly changing time zones, due to air travel.
The level of melatonin in the body is the highest during the night. It is interesting that people who work in darkened rooms also produce more melatonin than people who, for example, sunbathe intensely or work in places with strong light.
This gland will regularly produce melatonin only if it is healthy and if it is not poisoned by fluoride.
Due to its biochemical properties, it attracts the most fluoride from the body and if it is sufficiently poisoned by fluoride it will begin to calcify, then it works poorly.
Today’s scientists and psychotherapists claim that this gland is also the place where the gate of our higher being is hidden, the other side of our soul, the part that reacts to spiritual stimuli, which is turned exclusively to the other side.
Because nowadays we have completely rejected everything that does not come from technology and the real world, and it suffers, spoiling and literally getting dirty with waste and deposits of worries that we carry with us.
Thus, it is believed that almost every person today has some kind of cyst on the gland without even knowing it or discovering it at a routine magnetic resonance examination or examination performed for other reasons.
A cyst occurs for several reasons, although the real reason has not been determined to the end.
What does the pineal gland produce?
It is part of the endocrine system. Like the rest of the endocrine system, it is responsible for the production and regulation of hormones, most notably melatonin, vital to bodily function.
As brain mapping technology and scientific research expand, its function is becoming increasingly understood.
We now know that this is necessary for the overall health of the body, because it regulates the sleep cycle, without which essential healing and repair of the body cannot take place.
The gland is a small pine cone-shaped gland located deep in the brain where the two halves of the cerebrum meet. It is about the size of a grain of rice.
It is responsible for the production and secretion of melatonin, a hormone that is primarily used to regulate sleep patterns.
Melatonin production increases in the dark and decreases in the light, thus regulating the sleep cycle.
Interruption of the flow of information from light-sensing neurons can result in insomnia and other sleep disorders.
Melatonin is the primary hormone produced by the pineal; creates and regulates the circadian rhythm or 24-hour life cycle for humans.
Rhythm governs sleep and wakefulness, as well as diet and activity time or more active periods of brain waves.
A regulated pattern of sleep and wakefulness helps the body rebuild and replenish cells, fights infections, and engages in processes such as eating, drinking, and exercise that keep it healthy and functional.
Melatonin levels vary – they are produced less and less throughout the year, following a seasonal pattern. They also increase and decrease as the body changes, especially during puberty and menopause.
New research shows a link between the pineal and bone cell regrowth. Bone cells have M2 receptors that accept melatonin secreted by the gland.
This can stimulate bone growth while the body is at rest, and may also be part of the reason that melatonin secretion increases during puberty and during “growth acceleration” in children and teens.
The gland is outside the blood-brain barrier, making it unique among parts of the brain.
Furthermore, the concentration of blood supply within it is second only to the concentration in the kidneys.
The blood-brain barrier serves to protect parts of the brain from certain chemicals, including recreational and prescription drugs and alcohol.
The gland secretes hormones into the bloodstream, so it does not need a barrier. However, it also means that the gland can be affected by toxins and other chemicals from which the rest of the brain is protected, affecting the quality and amount of sleep.
What does your pineal gland do?
The function, as with any gland, secretion of hormones, this time melatonin, a very important hormone that affects sleep and wakefulness, and thus the functioning of the whole organism.
In essence, melatonin itself is secreted at night (that’s why children are told to grow while they sleep), which means that the organism recognizes when it is day and when it is night, possibly because of photoreceptors.
It does this in order to put the organism to sleep at night for rest, to introduce the body into puberty and the period of rapid growth, but also to initiate sexual drive and reproduction, in order for the individual to prolong the species.
It all depends on the assessment of the length of the day and night and the time that the body can spend in these conditions.
Recent research suggests that increased stress can lead to an accumulation of melatonin in the gland, leading to blockage of the ducts that are supposed to carry melatonin out or keep it inside the gland.
In that way, when it is enlarged, it can be dangerous for the surrounding tissue, because it presses the mass around it. Treatment of cystically alteration is carried out only if it is determined that the cyst is in some way dangerous for the organism.
In some cases, a biopsy is performed to rule out brain tumours, and if a cyst is found to be benign, the patient does not receive therapy.
Surgery is recommended only if a cyst or an enlarged gland is found to press on the surrounding tissue. In essence, it requires you to think about it and its health, as well as your own.
Try to stay away from stressful situations, find a way to calm down, at least in some parts of the day. Some theories say that it is desirable to spend more time in the sun and especially in the early morning hours to dedicate to meditation.
It is a fairly small gland, about the size of a grain of rice, that begins to appear and develop from the 7th week of pregnancy to the 2nd year of life, however its weight increases until adolescence.
This gland is largely associated with mental health, and one of its main functions is the production of melatonin. It is also called the regulator of the cycle and is responsible for performing various functions in the body.
The main function is the production of melatonin. Melatonin is a hormone responsible for regulating the sleep process, and it is also produced by serotonin.
As mentioned above, since it is responsible for the production of melatonin, it sends signals to the body that make us feel tired or sleepy at certain times of the day, as well as more active and awake.
It helps prevent some depressive or sleep disorders.
This gland also causes the production of certain hormones like endorphins that are responsible for increasing our happiness and emotional well-being in general.
The melatonin produced by this gland is associated with the skin tone that many species have.
This gland is associated with concentration and memory, affecting people’s cognitive functions. When it does not work properly, certain diseases can occur in the affected person.
The main mental disorders that can occur in this case would be sleep disorders when a person’s circadian rhythm changes.
On the other hand, there are depressive disorders by not releasing enough brain endorphins which, as we have seen, are hormones responsible for psychological well-being and happiness.
Poor functioning in bone mass production would lead to diseases such as severe bone deterioration.
When we have a deficiency or related problem, we can detect it if we pay attention to several symptoms that could indicate it.
After all of these pieces of information given about this very important gland, hopefully, the question at the beginning, "what does the pineal gland do?“ has been answered so it will be easier to understand how much of a big deal it is to our body.